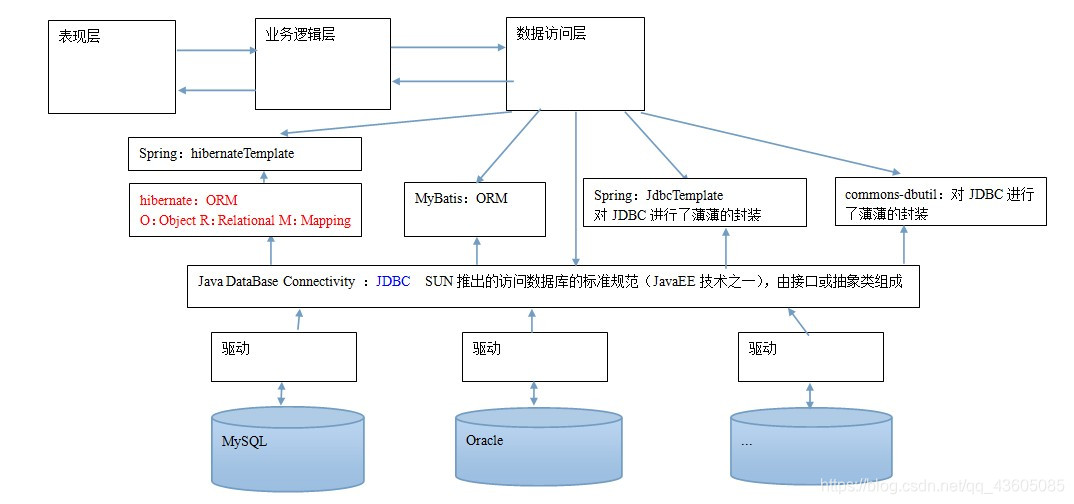
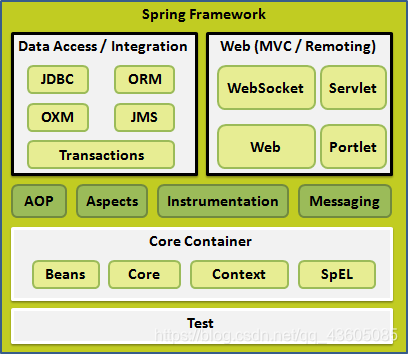
一、Spring中的JdbcTemplate 1、JdbcTemplate的概述 持久层总图:spring框架中提供的一个对象,是对原始Jdbc API对象的简单封装 。spring框架为我们提供了很多的操作模板类。并且我们需要导入spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar(它是和事务相关的)。
2、JdbcTemplate对象的创建 除了默认构造函数之外,其他的需要提供一个数据源DataSourc 。既然有set方法,依据我们之前学过的依赖注入,我们可以在配置文件中配置这些对象。
3、Spring中配置数据源 除了C3P0和DBCP数据源外,Spring还提供了内置的数据源 。
<bean id ="dataSource" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="root" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="xmgl0609" > </property > </bean >
3、JdbcTemplate中CRUD操作 (1)在bean.xml中配置JdbcTemplate对象进IOC容器
<bean id ="jdbcTemplate" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="dataSource" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="root" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="xmgl0609" > </property > </bean >
(2)利用JdbcTemplate对象基本使用
public static void main (String[] args) ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml" ); JdbcTemplate jt = ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate" , JdbcTemplate.class ) ; jt.execute("insert into account(name,money)values('ddd',2222)" ); }
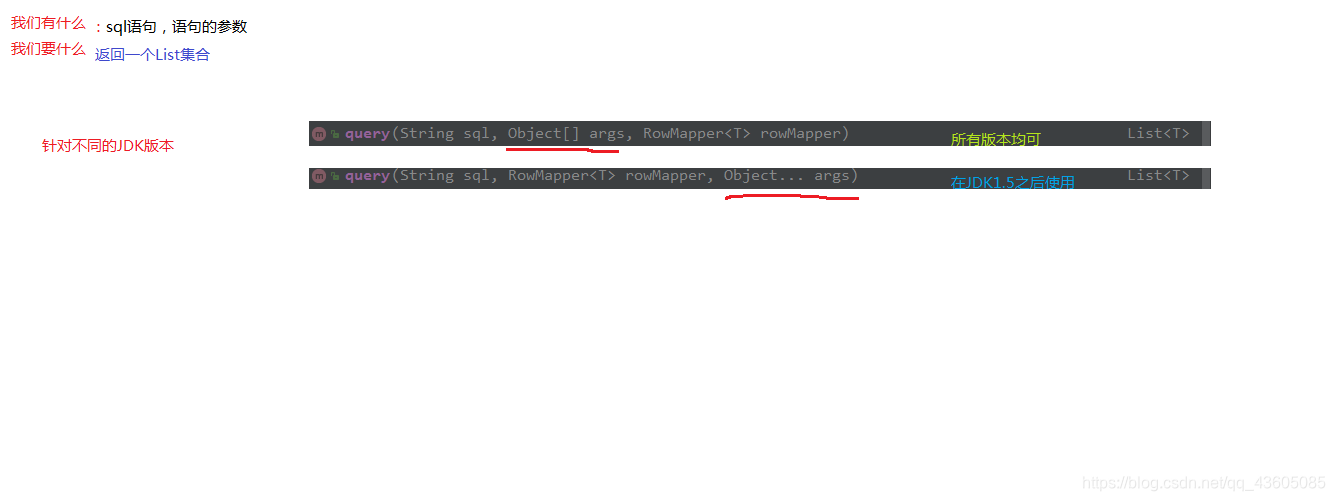
使用BeanPropertyRowMapper来封装结果集 查询所需的方法:
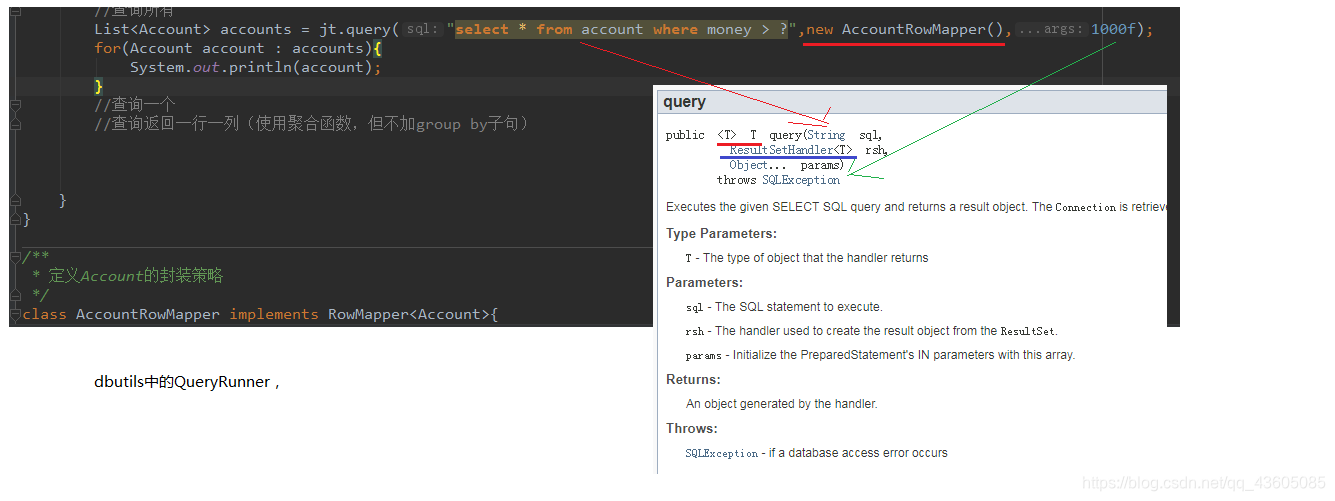
public static void main (String[] args) ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml" ); JdbcTemplate jt = ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate" , JdbcTemplate.class ) ; List<Account> accounts = jt.query("select * from account where money > ?" , new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class ), 100f ) ; for (Account account : accounts) { System.out.println(account); } new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class )来封装结果集 //查询一个 List <Account > accounts1 = jt.query("select * from account where id = ?" , new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class ), 100f ) ; System.out.println(accounts1.isEmpty()?"没有内容" :accounts1.get(0 )); }
jdbctemplate和queryrunner的区别:
4、JdbcTemplate应用到Dao层 对于是对数据库进行操作的对象,所以是在dao层。
jdbcTemplate.query ()
(1)第一种方式:在dao中定义并注入JdbcTemplate
public class IAccountDaoImpl2 implements IAccountDao private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate (JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) this .jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } @Override public Account findAccountById (Integer accountId) List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ? " , new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class ), accountId ) ; return accounts.isEmpty()?null :accounts.get(0 ); }
<bean id ="accountDao" class ="com.itheima.dao.impl.IAccountDaoImpl" > <property name ="jdbcTemplate" ref ="jdbcTemplate" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="jdbcTemplate" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean >
注意:有个小问题。就是我们的dao有很多时 ,每个dao都有一些重复性的代码。下面就是重复代码:
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void setJdbcTemplate (JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) this .jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; }
能不能把它抽取出来呢?dao继承JdbcDaoSupport
JdbcDaoSupport是spring框架为我们提供的一个类 ,该类中定义了一个JdbcTemplate对象,我们可以直接获取使用,但是要想创建该对象,需要为其提供一个数据源 。
public class JdbcDaoSupport private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate () return jdbcTemplate; } public void setJdbcTemplate (JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) this .jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; } public void setDataSource (DataSource dataSource) if (jdbcTemplate == null ) { jdbcTemplate = createJdbcTemplate(dataSource); } } private JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate (DataSource dataSource) return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource); } }
public class IAccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements IAccountDao @Override public Account findAccountById (Integer accountId) List<Account> accounts = super .getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where id = ? " , new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class ), accountId ) ; return accounts.isEmpty()?null :accounts.get(0 ); } @Override public Account findAccountByName (String accountName) List<Account> accounts = super .getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where name = ? " , new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class ), accountName ) ; if (accounts.isEmpty()) { return null ; } if (accounts.size() > 1 ) { throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一" ); } return accounts.get(0 ); } @Override public void updateAccount (Account account) super .getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set name = ? , money = ? where id = ?" ,account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId()); } }
两种方式有什么区别呢?
第一种在Dao类中定义JdbcTemplate的方式,适用于所有配置方式(xml和注解都可以)。
第二种让Dao继承JdbcDaoSupport 的方式,只能用于基于XML的方式,注解用不了。
二、Spring中的事务控制 1、Spring事务控制概述 第一:JavaEE体系进行分层开发,事务处理位于业务层,Spring提供了分层设计业务层的事务处理解决方案。
第二:spring框架为我们提供了一组事务控制的接口 。具体在后面的第二小节介绍。这组接口是在spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar中。
第三:spring的事务控制都是基于AOP(事务操作抽取出来)的 ,它既可以使用编程的方式实现,也可以使用配置的方式实现。我们学习的重点是使用配置的方式实现。
2、Spring中事务控制的API介绍 (1)PlatformTransactionManager
此接口是spring的事务管理器 ,它里面提供了我们常用的操作事务的方法,我们在开发中都是使用它的实现类。
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager 使用Spring JDBC或iBatis 进行持久化数据时使用 org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager 使用Hibernate版本进行持久化数据时使用
(2)TransactionDefinition
REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)
SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(一般查询操作时使用,没有事务)
(3)TransactionStatus:此接口提供的是事务具体的运行状态,方法介绍如下图:
3、基于XML的声明式事务控制(配置方式)重点 (1)在spring的配置文件并导入约束
此处需要导入aop和tx两个名称空间 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd" > <bean id ="dataSource" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="root" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="xmgl0609" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="accountDao" class ="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="accountService" class ="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl" > <property name ="accountDao" ref ="accountDao" > </property > </bean > </beans >
(2)dao层和service层(略)不使用 AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport ,来实现。而选择注入JdbcTemplate对象,引入DataSource。
(3)
Spring中基于xml的声明式事务控制配置步骤 1.配置事务的管理器(DataSourceTransactionManager)
<bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean >
2.配置事务的通知 <tx:advice id ="txAdvice" transaction-manager ="transactionManager" > <tx:attributes > <tx:method name ="*" propagation ="REQUIRED" read-only ="false" /> <tx:method name ="find*" propagation ="SUPPORTS" read-only ="true" /> </tx:attributes > </tx:advice >
此时我们需要导入事务的约束 tx名称空间和约束,同时需要AOP给事务通知提供试图管理器引用
配置事务的属性
propagation=”” 用于指定事务的传播行为。默认值是REQUIRED,表示一定会有事务,增删改的选择。查询方法可以选择SUPPORTS。 read-only=”” 用于指定事务是否只读,只有查询方法,才是设置为true。默认是false,表示读写
isolation=”” :用于指定事务的隔离级别。默认是DEFAULT,表示使用数据库的默认隔离级别
3.配置AOP中的通用切入点表达式事务通知 和切入点表达式 的对应关系
<aop:config > <aop:pointcut id ="pt1" expression ="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))" /> <aop:advisor advice-ref ="txAdvice" pointcut-ref ="pt1" > </aop:advisor > </aop:config >
4、基于注解的配置方式 (1)导入约束,配置数据源DataSource,配置JdbcTemplate导入DataSource ,将service层和dao层交给spring管理
Spring中基于注解 的声明式事务控制配置步骤 1.配置事务管理器
<bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean >
2.开启spring对注解事务的支持
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager ="transactionManager" > </tx:annotation-driven >
3.在需要事务支持的地方(service层)使用@Transactional注解
@Service ("accountService" )@Transactional (propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS,readOnly = true )public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService @Autowired private IAccountDao accountDao; @Override public Account findAccountById (Integer accountId) return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId); } @Override @Transactional (propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly = false ) public void transfer (String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) System.out.println("transfer...." ); Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName); Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName); source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money); target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money); accountDao.updateAccount(source); int i=1 /0 ; accountDao.updateAccount(target); } }
该注解的属性和xml中的属性含义一致 。出现在类上,表示类中所有方法有事务支持 出现在方法上,表示方法有事务支持。
以上三个位置的优先级:方法>类> 接口
5、不使用xml的配置方式 @EnableTransactionManagement ,加上表示该类是事务管理。
@Configuration @ComponentScan ("com.itheima" )@Import ({JdbcConfig.class ,TransactionConfig .class }) @PropertySource("jdbcConfig.properties") @EnableTransactionManagement public class SpringConfiguration }